Struggling to Catch Your Breath? A Simple Breathing Test Might Help
Tight Chest and Breathing Difficulty: Understanding the Symptoms
Experiencing a tight chest and breathing difficulty can be alarming, especially when these symptoms occur unexpectedly. These sensations are often described as a feeling of constriction or pressure in the chest, making it hard to take a deep breath. While these symptoms can be associated with various conditions, they often indicate some form of respiratory issue.
Common causes of these symptoms include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or even anxiety. In asthma, the airways narrow and swell, producing extra mucus which can lead to breathing difficulties. COPD, a progressive disease, causes airflow blockage and breathing-related problems. Anxiety, on the other hand, can trigger hyperventilation, leading to a sensation of tightness in the chest.
It’s crucial to pay attention to these symptoms, especially if they persist or worsen over time. They can be a sign of reduced lung function, which might require medical evaluation. Consulting a healthcare professional is advised to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment. A spirometry breathing test can be an invaluable tool in diagnosing these issues.
Understanding the Spirometry Breathing Test
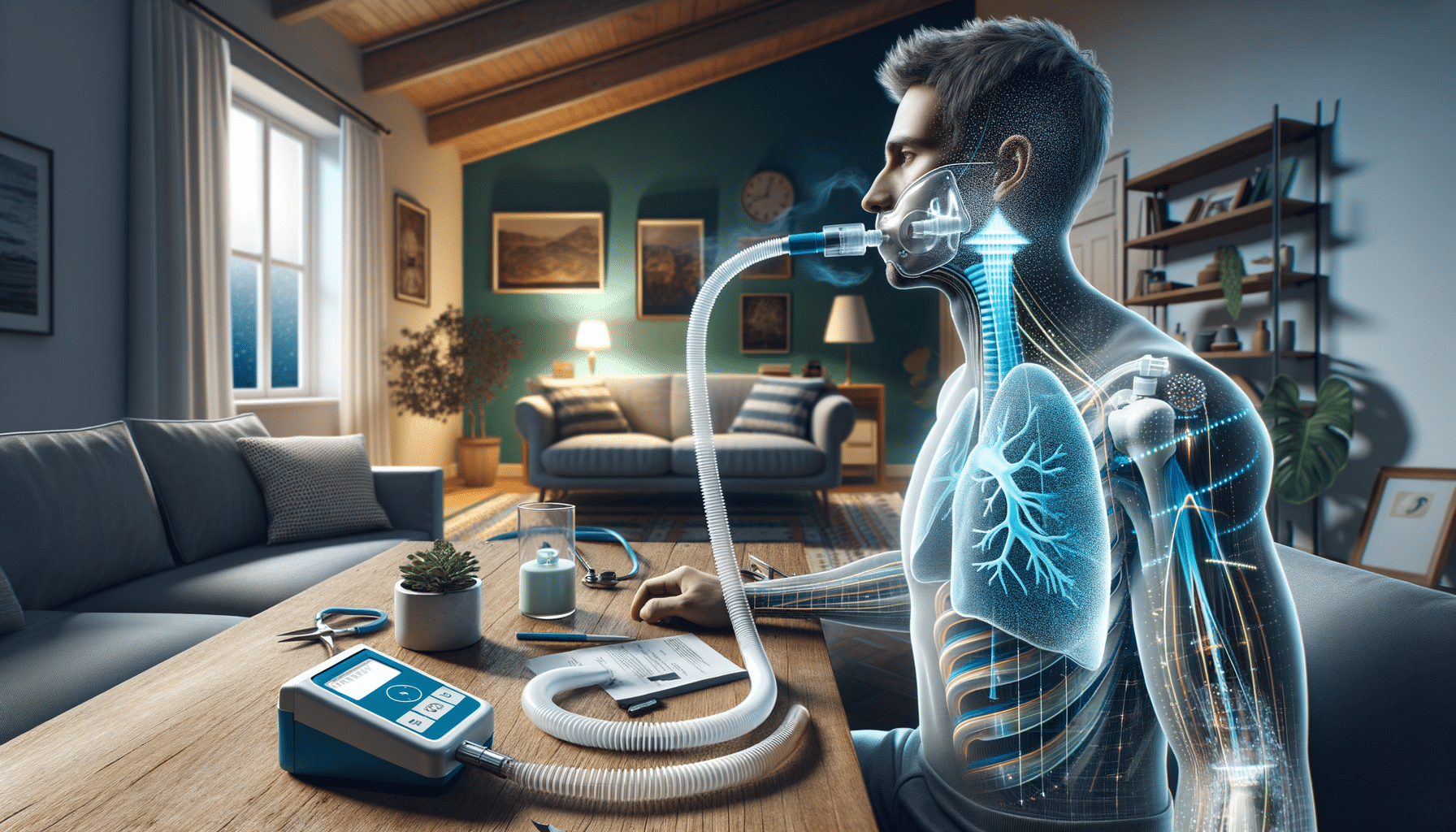
The spirometry breathing test is a common and effective method used to assess lung function. It measures how much air you can inhale and exhale, as well as how quickly you can exhale. This test is crucial in diagnosing conditions like asthma, COPD, and other respiratory disorders.
During the test, you’ll be asked to breathe into a mouthpiece connected to a spirometer, a device that records the amount and rate of air you breathe in and out over a specified period. The results provide valuable insights into your lung capacity and the presence of any obstructions in the airways.
Spirometry is often recommended for individuals experiencing symptoms such as persistent cough, wheezing, or shortness of breath. It’s also used to monitor the lung function of patients with chronic respiratory diseases, helping to assess the effectiveness of treatment plans. By understanding your lung function, you can take proactive steps in managing your respiratory health.
Breathing Tests You Can Perform at Home
While professional medical tests like spirometry are essential for accurate diagnosis, there are simple breathing tests you can perform at home to monitor your lung health. These tests are not a substitute for professional evaluation but can help you track changes in your respiratory function.
One basic test you can try is the Peak Flow Meter test. This handheld device measures how well air moves out of your lungs. To use it, you simply blow into the device as hard and fast as you can. Regular monitoring with a peak flow meter can help you detect changes in your lung function, indicating when you might need to seek medical advice.
Another method is the breath-holding test, where you take a deep breath and see how long you can hold it. This can give a rough indication of your lung capacity. However, it’s important to note that these home tests should not replace medical evaluations. If you notice significant changes or persistent symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive assessment.